Tyres & rubber
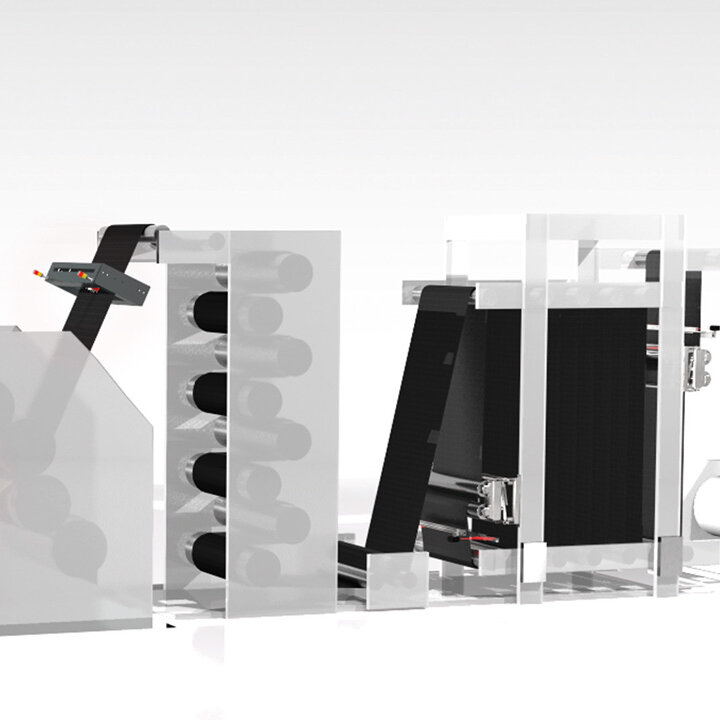
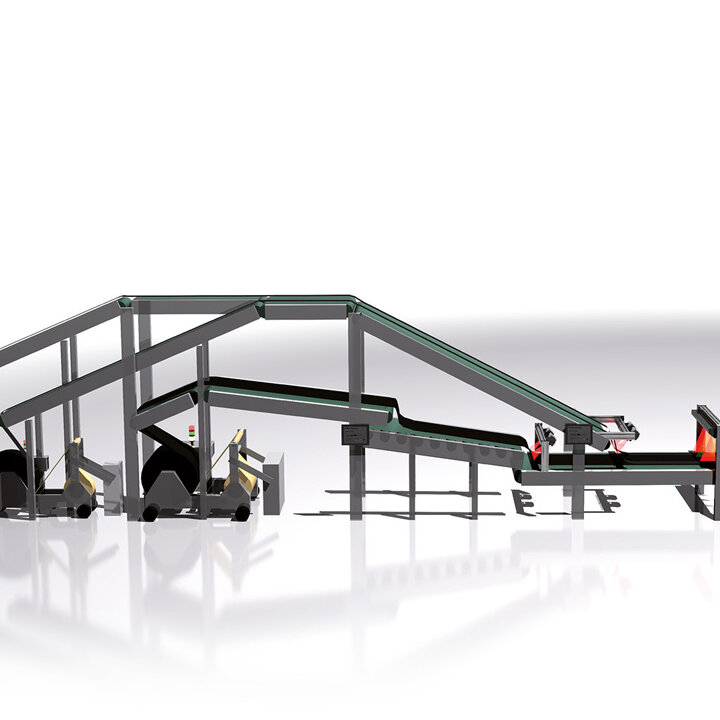
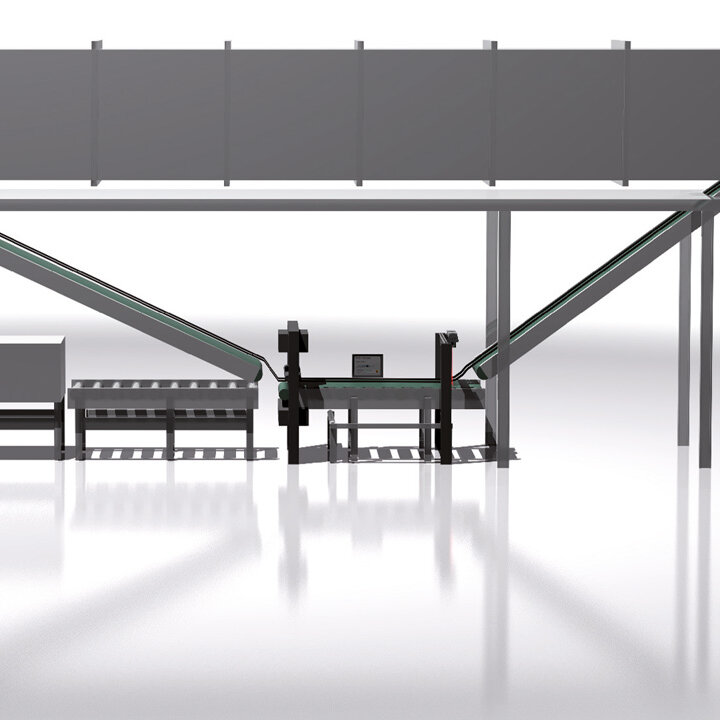
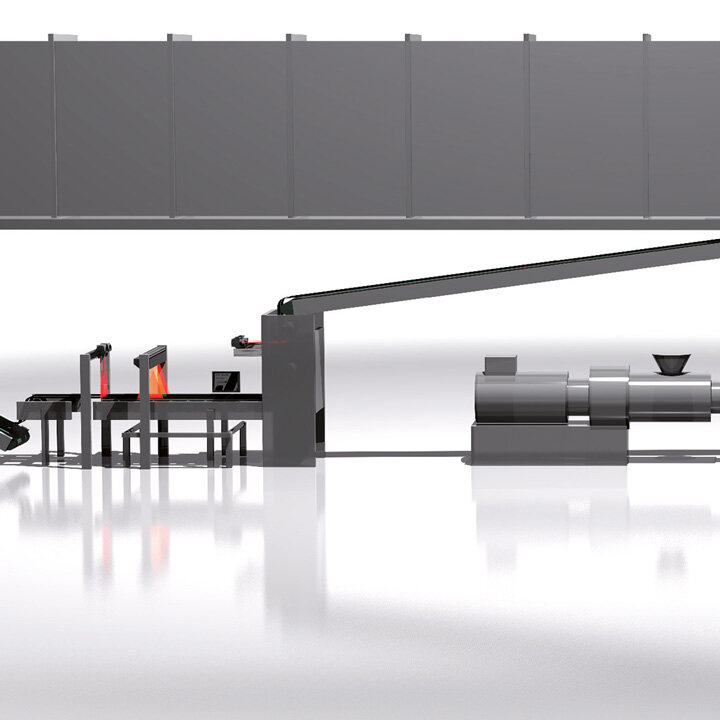
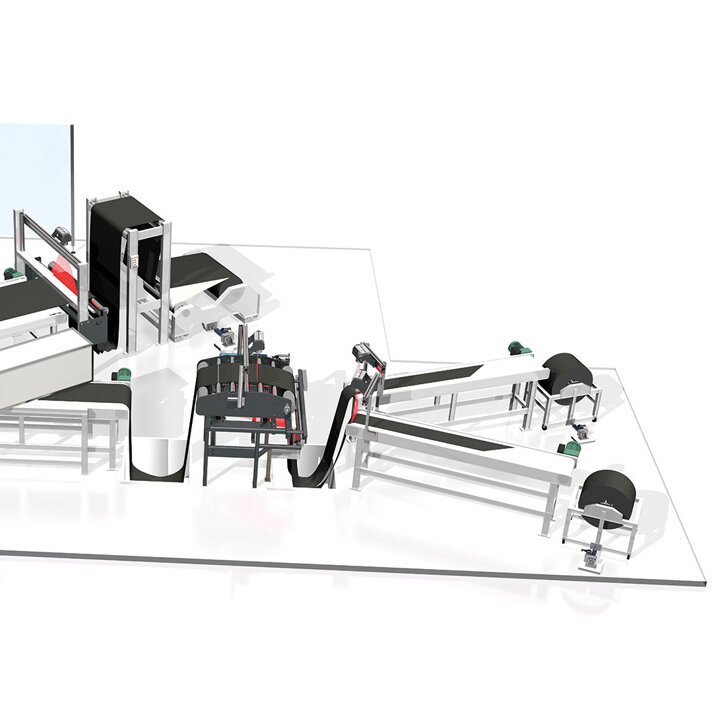
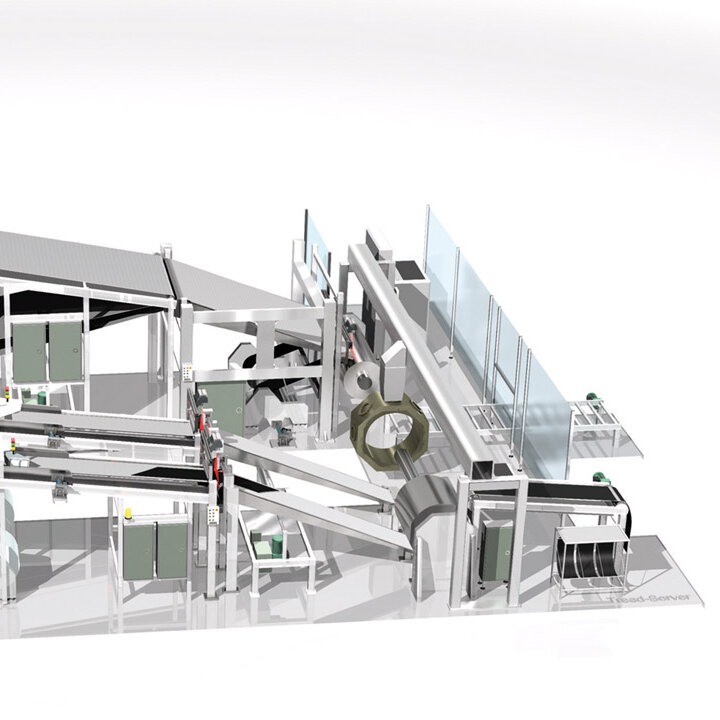
The demands on control and inspection systems are increasing as a result of the progressive automation of manufacturing processes in tire production in the automotive industry, as well as the continuously increasing expectations for product quality. BST has many years of experience and can provide lean automation solutions, intelligent quality assurance systems, and cutting-edge control components to solve upcoming automation problems. BST develops application-specific solutions for new applications and retrofits in addition to standard products – Perfecting your Performance.